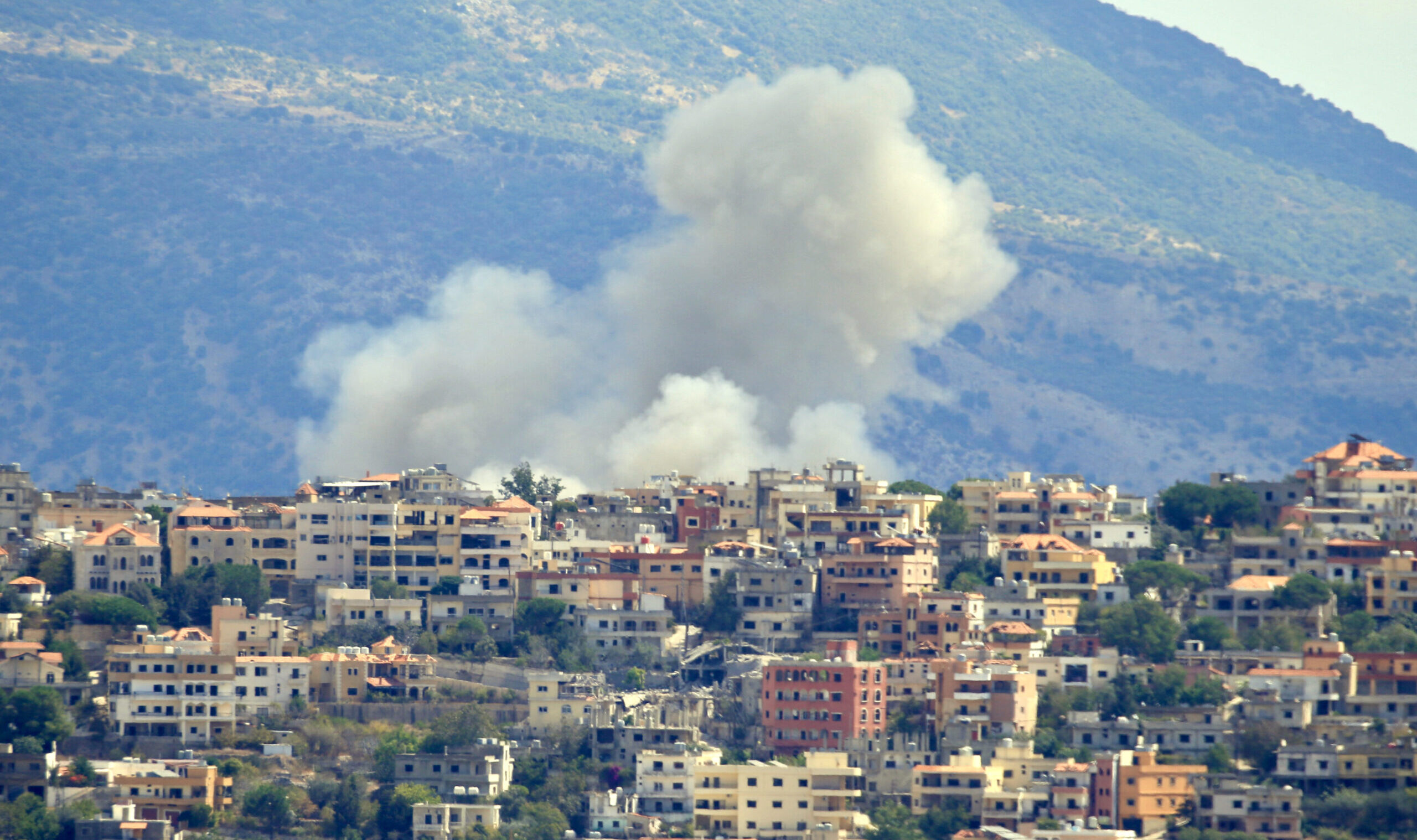
On the matter of a resolution calling for an immediate humanitarian cease-fire in Gaza, the United Nations General Assembly conducted a vote. The resolution aimed to address the ongoing conflict and ensure the safety and well-being of the affected population.
The outcome of the vote was notable, with an overwhelming majority of 153 countries voting in favor of the resolution. This demonstrated the widespread international support for an immediate cessation of hostilities and the urgent need for humanitarian assistance.
The United States and Israel were among the 10 countries that voted against it, while Germany was among the 23 that abstained.
You may be interested
Here is a map of the vote in the UN General Assembly on a resolution demanding an immediate humanitarian cease-fire in Gaza.
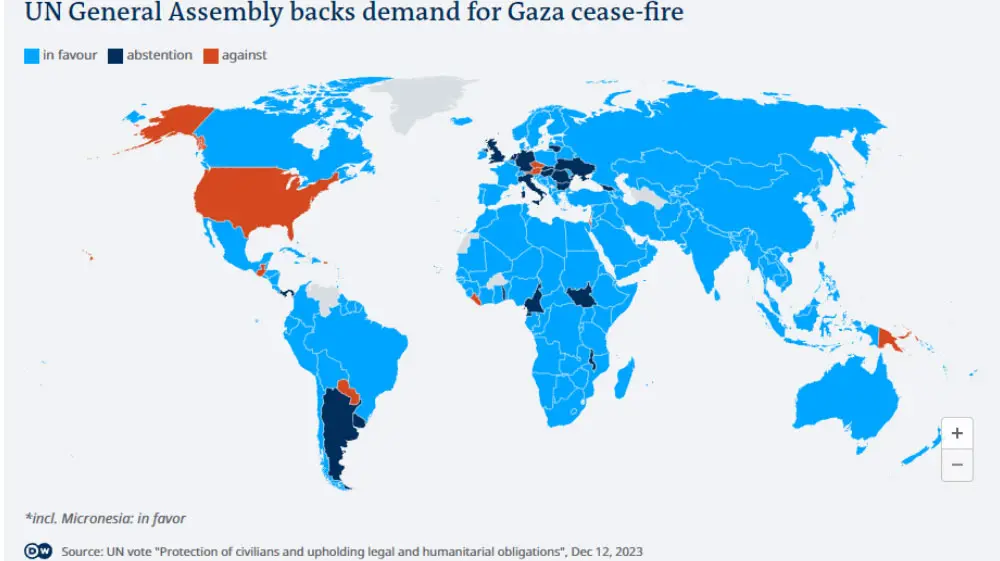
Germany was among the 23 countries that abstained from voting. Abstentions often indicate a reluctance to take a position or a desire to maintain neutrality in a contentious issue.
The vote in the UN General Assembly highlights the complex dynamics surrounding the conflict in Gaza. While the majority of nations expressed their support for a humanitarian cease-fire, the differing positions of some countries underscore the challenges in finding a consensus solution.
While it is challenging to provide specific details on the economic problems faced by the 10 countries that voted against the resolution demanding an immediate humanitarian cease-fire in Gaza, we can analyze some general factors that may have influenced their decision.
- National Interests: Countries often prioritize their national interests when making decisions on international matters. Economic considerations, such as trade relationships, investment opportunities, or geopolitical alliances, can play a significant role in shaping a country’s stance on a particular issue.
- Political Considerations: Domestic political factors can also influence a country’s voting decision. Governments may take into account public opinion, political ideologies, or the potential impact on their domestic political landscape when deciding how to vote on a resolution.
- Regional Dynamics: Countries in the same region may have shared concerns or interests that influence their voting patterns. Regional alliances, historical conflicts, or geopolitical rivalries can shape a country’s position on international resolutions.
- Humanitarian Aid: While the resolution aimed to address the humanitarian situation in Gaza, countries may have different perspectives on the most effective approach to providing aid. Some countries may prefer alternative channels or mechanisms for delivering humanitarian assistance, which could have influenced their decision to vote against the resolution.
- Perceived Implications: Countries may have had concerns about the potential consequences or implications of the resolution. These concerns could be related to issues such as sovereignty, national security, or the effectiveness of the proposed cease-fire in achieving a lasting solution to the conflict.
It is important to note that the specific economic problems faced by the 10 countries that voted against the resolution may vary significantly. Detailed analysis of each country’s economic situation, trade relationships, and geopolitical context would be necessary to provide a comprehensive understanding of their specific economic challenges.
It is important to note that the UN General Assembly resolutions are non-binding and serve as expressions of international opinion. They aim to raise awareness, encourage dialogue, and facilitate diplomatic efforts. The resolution’s adoption by an overwhelming majority reflects the global concern for the humanitarian situation in Gaza and emphasizes the need for a peaceful resolution to the conflict.













